India’s Economic Slowdown and GDP Growth Rate 2024-25: UPSC Prelims Pointer
India’s Economic Slowdown and GDP Growth Rate 2024-25: Detailed Analysis
Introduction
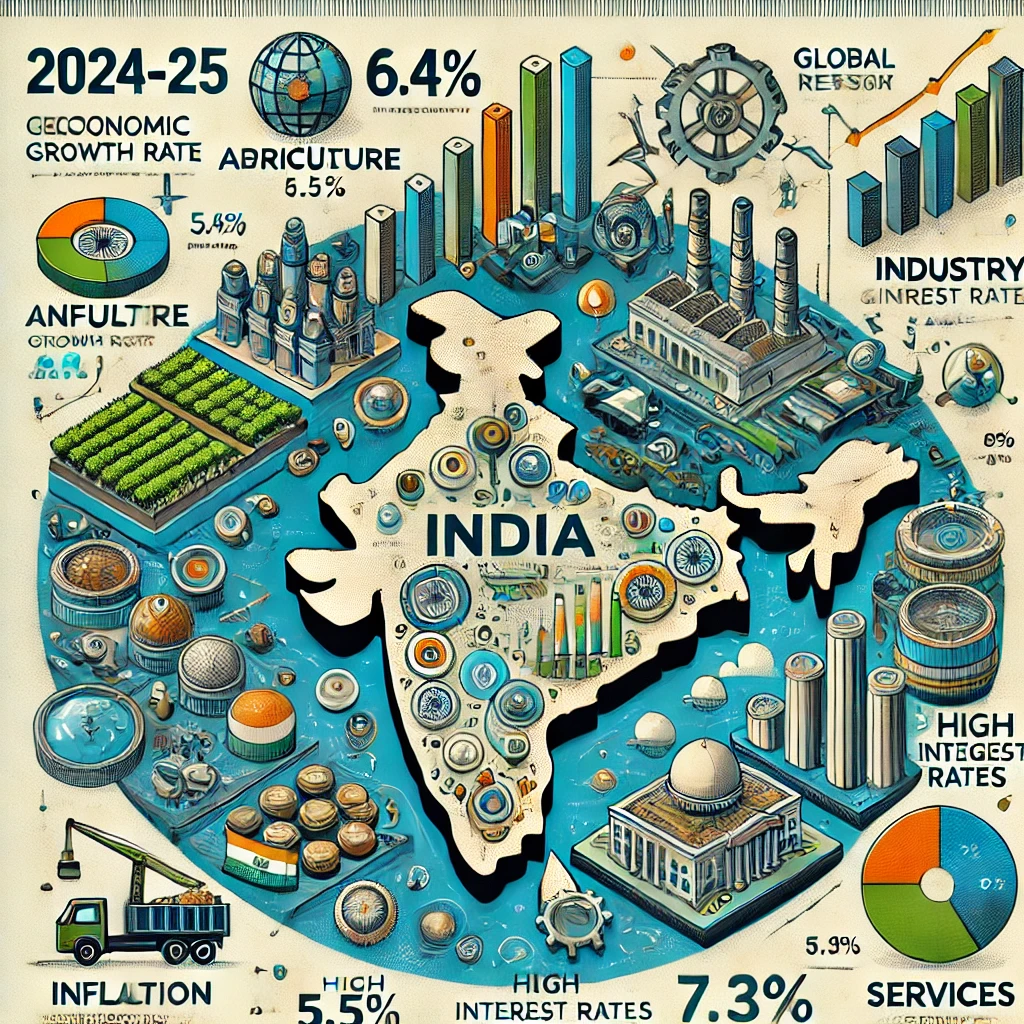
According to the first advance estimates released by the National Statistical Office (NSO), India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate for 2024-25 is projected at 6.4%, marking a four-year low. This slowdown is attributed to several domestic and global factors and reflects challenges in consumer demand, industrial output, and job creation.
Key Indicators and Statistics
| Indicator | 2024-25 | 2023-24 | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate | 6.4% | 7.2% | Lowest in four years, signaling economic deceleration. |
| Agriculture Growth Rate | 3.5% | 3.9% | Impacted by uneven monsoons and climate change. |
| Industrial Growth Rate | 5.2% | 5.8% | Decline in manufacturing and construction activity. |
| Services Growth Rate | 7.3% | 9.1% | Slowdown in financial and IT services. |
| Inflation (CPI) | 5.4% | 5.8% | Decline in consumer spending due to higher prices. |
Causes of Economic Slowdown
1. Domestic Factors
- Inflationary Pressures:
- Rising prices of essential commodities.
- Reduced purchasing power, especially in rural and urban middle-class households.
- Increase in Interest Rates:
- Repo rate at 6.5%: Higher borrowing costs discouraged consumer and corporate investments.
- Decline in Private Investments:
- Private sector investments slowed due to economic uncertainties.
- Employment Issues:
- Limited job creation in both formal and informal sectors.
2. Global Factors
- Global Economic Slowdown:
- Economic deceleration in the US, Europe, and China negatively impacted Indian exports.
- Weak global demand reduced manufacturing output.
- Ukraine-Russia Conflict:
- Disruptions in the supply chain and volatility in energy prices.
- Increased costs of raw materials and imports.
- Depreciation of the Rupee:
- The Indian rupee weakened against the US dollar, making imports more expensive and widening the trade deficit.
Impact of the Slowdown
1. On Consumers
- Decline in Household Spending:
Higher inflation and reduced incomes strained household budgets. - Rising Unemployment:
Fewer job opportunities added financial pressure on families.
2. On Businesses
- MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises):
High borrowing costs and weak demand put small businesses at risk of closure. - Export Sector:
Declining global demand added pressure on exporters.
3. On the Government
- Fiscal Deficit:
Lower tax revenue and increased spending on welfare schemes may widen the fiscal deficit. - Policy Pressure:
The government faces the challenge of reviving growth while maintaining fiscal discipline.
Measures to Address the Slowdown
1. Domestic Reforms
- Boost Consumer Demand:
- Expand programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA).
- Provide direct financial support to low-income households.
- Support for MSMEs:
- Ensure affordable credit for small businesses.
- Offer tax incentives and financial assistance to MSMEs.
- Invest in Infrastructure:
- Accelerate infrastructure projects to create jobs and stimulate economic activity.
2. Expand Global Trade
- Strengthen Exports:
- Expand the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to new sectors.
- Focus on signing Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) to diversify export markets.
- Promote Green Energy:
- Invest in renewable energy projects, including solar and wind power.
- Strengthen energy security through domestic production.
3. Maintain Financial Stability
- Control Inflation:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) must implement balanced monetary policies to keep inflation in check. - Improve Tax Revenue:
Rationalize Goods and Services Tax (GST) rates and enhance compliance mechanisms.
Conclusion
India’s economic slowdown in 2024-25 reflects short-term challenges arising from domestic and global uncertainties. However, with strong policy interventions, structural reforms, and targeted investments, the country can overcome these hurdles and regain its growth trajectory.
Proactive measures to boost demand, support industries, and diversify exports are essential to restore economic stability and ensure inclusive growth. While the slowdown presents immediate challenges, India’s long-term economic potential remains robust.


 Learn With MS
Learn With MS
Post Comment